GNOME Log Viewer
Linux versions that are Ubuntu based have a built in GUI application for viewing logs. This app is simply called Logs in the Ubuntu interface and is very similar to the one that is used by Mac but often lacks a lot of the controls that are useful when it comes to logging. To navigate to the logs application in Ubuntu, select the Show Applications icon in the dock.
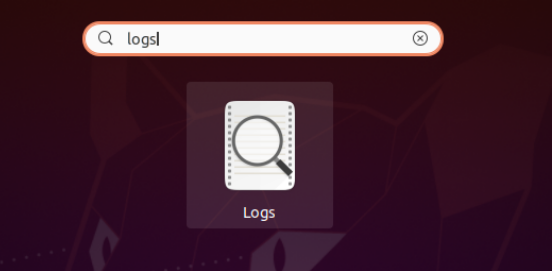
From here, type in “logs” and select the logs application.
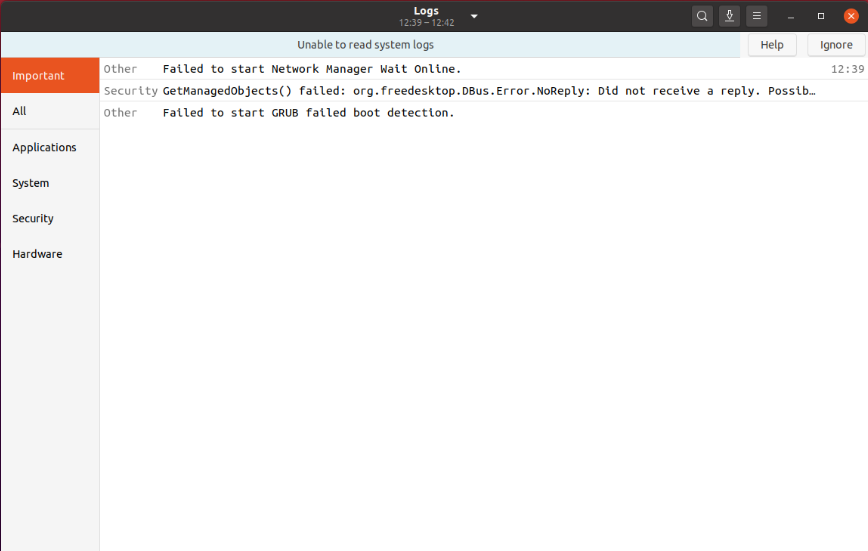
Upon launching, the logs main/home screen will show. The log application interface is fairly straightforward and simple. The application generally launches on the important tab, which will show only the few most important logs, such as major errors.
The “All” tab is a list of all the events from the logs compiled and then sorted in order of time. This is a good way to see all the events at a particular time. The Applications, System, Security, and Hardware tabs are all a list of the events that relate to that particular topic. For example, the Applications tab shows information relating to the computers applications such as launching and minor tasks they do.
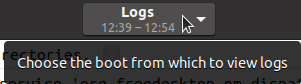
The top of the logs window displays a drop down option. This option allows the user to select which logs they want to view from which boot of the machine. By default, this is set to the current machine boot log.
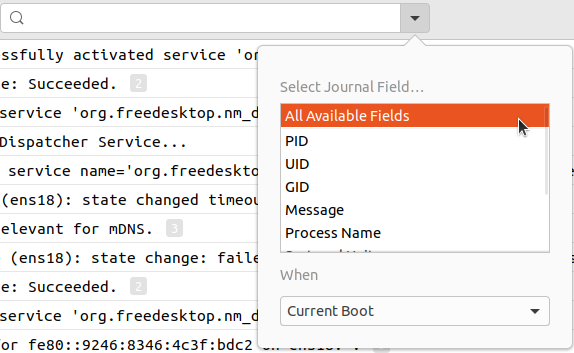
In the top right of the application window, there are three options. Number 1 is the search function and allows a user to search for a particular string in the log file. You can also press control and F to activate the search function.
Number 2 gives the user the option to export the logs to a file. Finally, Number 3 gives the user the option to open a new window, get help, or gain info about the application. The logs application is not a great application for viewing logs due to restrictions such as not being able to search for a term that has spaces in it.
