Windows Starting Up
Enabled by default
Service: Microsoft Windows Security Auditing
Log type: Security
The Windows System Starting up is self explanatory in name. It may indicate a system being restarted after an attack or to load malicious software. In general, it is good to know when systems are being started.
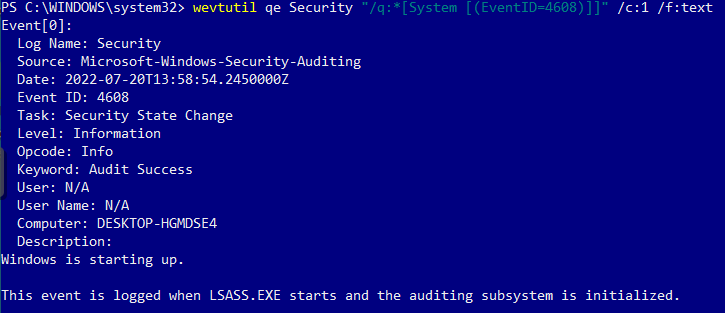
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashTable @{LogName='Security';ID='4608'} -MaxEvents 1 | Format-Listauditpol /get /subcategory:"Security State Change"
auditpol /set /subcategory:"Security State Change" /Success:Disable /Failure:Disable
auditpol /set /subcategory:"Security State Change" /Success:Enable /Failure:Enable
Compliance
HIPAA
Level: Recommended
PCI DSS
Level: Required
https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/documents/PCI_DSS_v3-2-1.pdf?agreement=true&time=1631643252599
NSA Event Forwarding
Level: Recommended
https://github.com/nsacyber/Event-Forwarding-Guidance/tree/master/Events
In order to enable auditing on Windows starting events, navigate to the System Audit Policies in the group policy editor. Enable 'Security State Change' under the System tab.
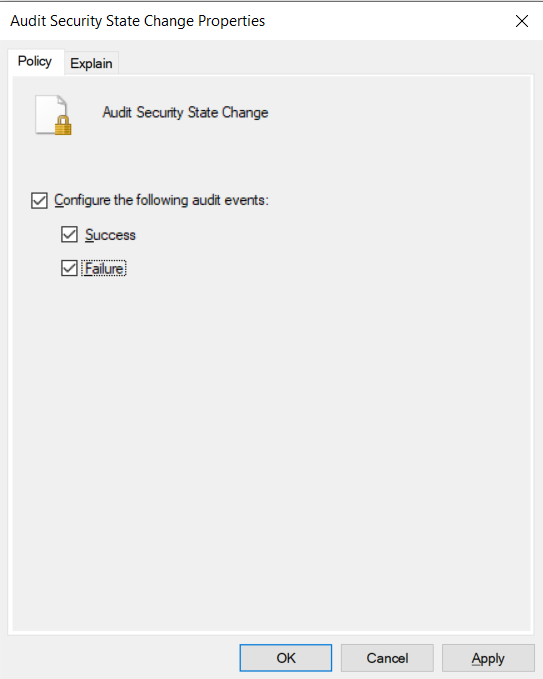
This is not logged by default on the Windows system and falls under the "Security State Change" category. In order to turn on auditing for this event, enter the command auditpol /set /subcategory:"Security State Change" /Success:Enable /Failure:Enable

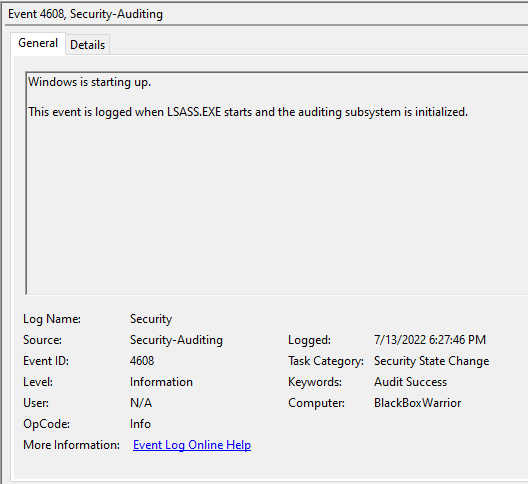
Changes to the audit policy are logged by default in Windows 10 Professional. To view the logs, navigate to the Event Viewer Security tab and sort of filter by Event ID 4608.
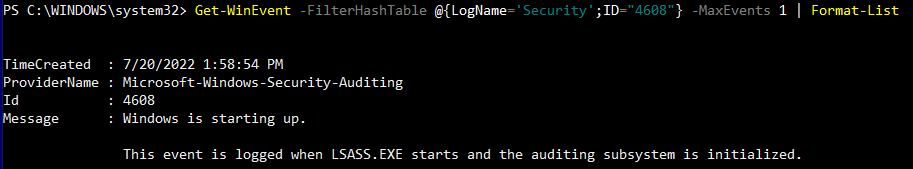
To view this log in the command line with Get-WinEvent, open PowerShell as an administrator. From here, enter the command Get-WinEvent -FilterHashTable @{LogName='Security';ID='4608'} -MaxEvents 1 | Format-List
To view this log in the command line with wevtutil, open PowerShell or Command Prompt as an administrator. From here, enter the command wevtutil qe Security "/q:*[System [(EventID=4608)]]"