Failed User Logon
Enabled by default
Service: Microsoft Windows security auditing
Log type: Security
Failed user logins can show possible password spray and password guessing attacks. Not every failed login is an attack, but they can be early indicators of one. This log is required by the PCI DSS regulation and is recommended by the NSA Cyber Event Forwarding Guidance.
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashTable @{LogName='Security';ID='4625'} -MaxEvents 1 | Format-Listauditpol /get /subcategory:"logon"
auditpol /set /subcategory:"logon" /Success:Disable /Failure:Disable
auditpol /set /subcategory:"logon" /Success:Enable /Failure:Enable
Compliance
HIPAA
Level: Recommended
PCI DSS
Level: Required
https://www.pcisecuritystandards.org/documents/PCI_DSS_v3-2-1.pdf?agreement=true&time=1631643252599
NSA Event Forwarding
Level: Recommended
https://github.com/nsacyber/Event-Forwarding-Guidance/tree/master/Events
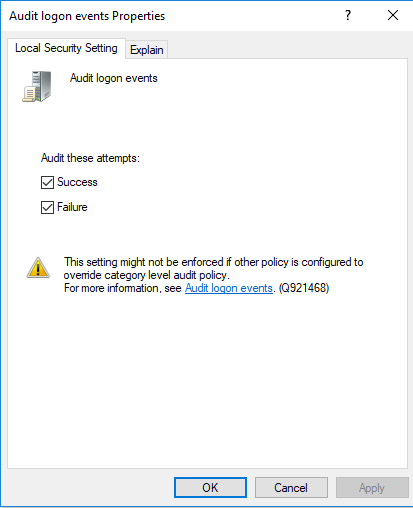
Windows 10 Professional does not log this by default. To enable logging of this activity, launch the Group Policy Editor. From here, expand the Windows settings folder and open the Security Settings tab. Finally, expand the Local Policies tab and click to enter the Audit Policy header. In order to turn on login auditing, double click "Audit login events". Clicking the Success box will allow for the auditing of all successful login attempts.
To view this log in the Event Viewer, open the event viewer and navigate to the Windows Logs heading and then the Security Tab. From here, select the find function and search for the value 4625 , or filter the log for the ID 4625.

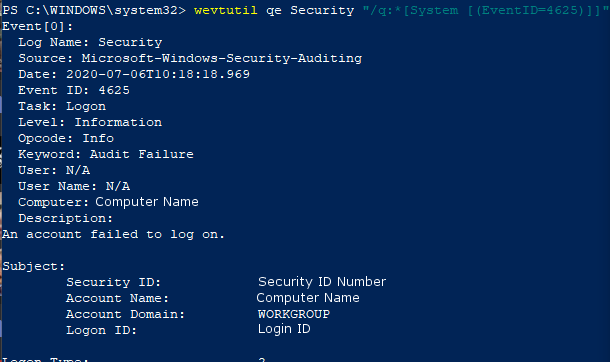
To view this log in the command line with Get-WinEvent, open PowerShell as an administrator. From here, enter the command Get-WinEvent -FilterHashTable @{LogName='Security';ID='4625'} -MaxEvents 1 | Format-List
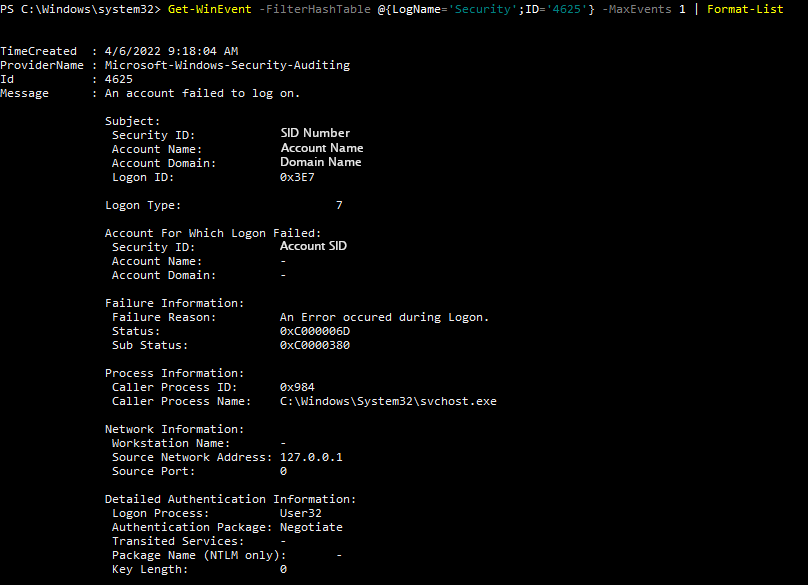
To view this log in the command line with wevtutil, open PowerShell or Command Prompt as an administrator. From here, enter the commandwevtutil qe Security "/q:*[System [(EventID=4625)]]"